The days of not knowing a website’s full security protocols are over.
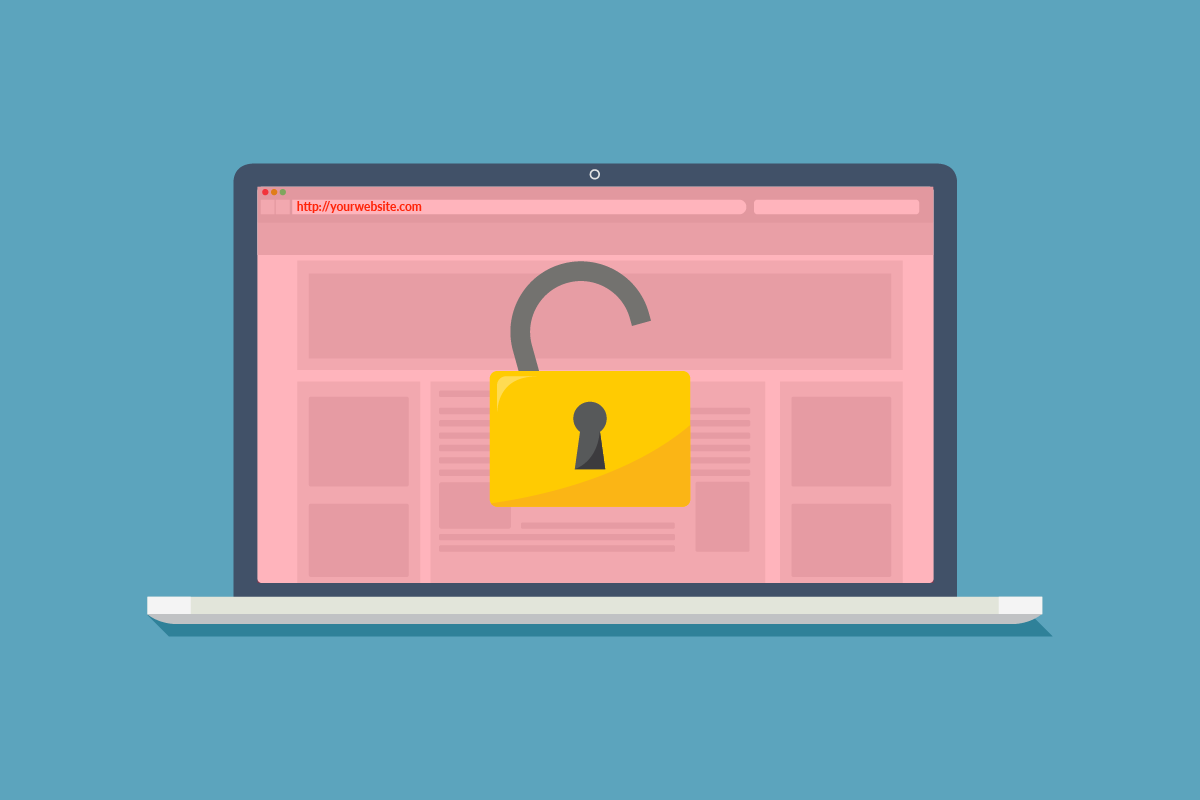
Have you noticed the “Not Secure” label in Google Chrome recently? If you have, it means websites are using the old HTTP security protocol, and that could soon hurt your business.
What’s changed: the address bar used to show a simple “I” icon to the left of the address in order to show that the site was not utilizing a secure browsing protocol—otherwise known as HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol – Secure). When you clicked on the icon, it would clearly display “Your connection to this site is not secure” and give further information into why that might be.
Below is an example of what you’re likely seeing:
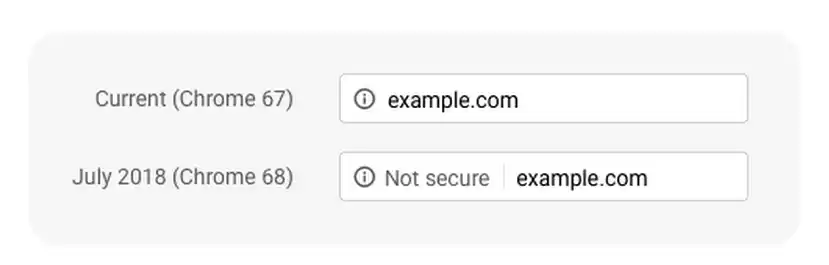
As of Chrome 68, which was released late in July 2018, the “I” icon had an additional “Not Secure” text in its place if the website was using an HTTP connection, which is by nature not secure. This is part of Google’s substantial push to get the entire web using HTTPS.
What is HTTPS Encryption?
In a nutshell, HTTP was the baseline transfer protocol that the worldwide web was built on. It provided a seamless way for folks to request information from a server and then have that server display what was requested (i.e. the website).
After a few years of building the web around this protocol, it became clear to many that this method, while fast and convenient, was insecure. Successful hackers were able to tamper with the traffic by injecting their malicious code during the transfer stream to either redirect folks to a different (read: malicious) lookalike page, spy on their web behavior, or steal valuable information.
As a result of these malicious attacks, a secure version of this protocol was created to protect user information; hence HTTPS.
Why Does Google Want HTTPS?
Google recently stated in a blog post that “Security has been one of Chrome’s core principles since the beginning—we’re constantly working to keep you safe as you browse the web. Nearly two years ago, we announced that Chrome would eventually mark all sites that are not encrypted with HTTPS as ‘not secure’. This makes it easier to know whether your personal information is safe as it travels across the web, whether you’re checking your bank account or buying concert tickets.”
This goes to show that Google takes security seriously, even if it’s an added expense for other businesses.
How Does This Affect Your Business?
With approximately 62% of the world’s web viewers using a Chrome browser in December 2018, your business is highly susceptible to being flagged as “Not Secure” if you don’t already have HTTPS on your website.
The great news is that there are sources like Let’s Encrypt out there that make it fairly easy to get HTTPS enabled on your website.
Not only will this assure your website visitors that their information is safe, HTTPS is even being used as a ranking signal for Google. So, you could effectively boost your organic PageRank just by enabling HTTPS on your website.
If you haven’t already enabled HTTPS on your own business website, we highly recommend it. The benefits outweigh the small costs and can save many headaches in the future.
Helpful Resources:
HTTP Showing as ‘Not Secure’ in Chrome 68: https://www.blog.google/products/chrome/milestone-chrome-security-marking-http-not-secure/
HTTPS as a Ranking Signal: https://webmasters.googleblog.com/2014/08/https-as-ranking-signal.html
Free SSL Certificate: https://letsencrypt.org/





